SQL Server CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() Function
In SQL Server, the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() function returns the current system timestamp of the server on which the SQL Server database instance is installed. It is returned as a datetime value without the time zone offset.
Note: The CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() function is the ANSI equivalent to the GETDATE() function.
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP()Parameters
No parameters.
Return Value
Returns current system timestamp of the server of datetime data type in YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.mmm format.
Note: You can use the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP function anywhere a DATETIME expression.
Get Current DateTime Stamp
In the following example, the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() is used to get the current date and time value of the server hosting the SQL Server database instance.
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP AS CurrentServerDateTime;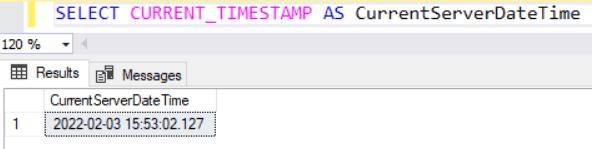
Use Current_TimeStamp as Default Value
In the following example, the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is used as a default value of a column.
Create a new table tblEmployeeLogin as shown below. This table captures the EmployeeId and the current date-time when an employee logs in. Here, the column EmpLogin takes the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP as its default value. It stores the timestamp as DateTime when an employee logs into the server.
CREATE TABLE tblEmployeeLogin
(
id INT IDENTITY,
EmployeeID INT NOT NULL,
EmpLogin DATETIME NOT NULL
DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);Now, when an employee logs in then we will insert a new row into the tblEmployeeLogin table , as shown below. Assume that an employee with id 2 is logged in.
INSERT INTO tblEmployeeLogin(EmployeeID) VALUES(2);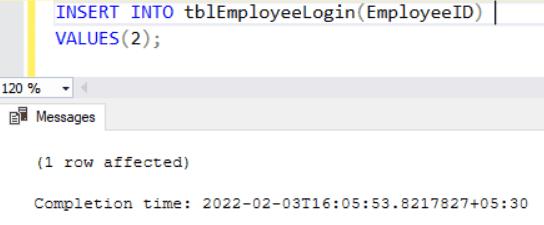
Now, let's check the data. Select rows from the table and you will see that the EmpLogin column has the datetime stamp when the new row was inserted into the tblEmployeeLogin table.
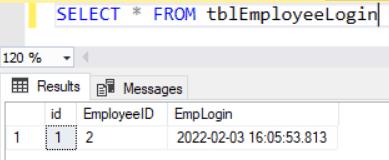
Thus, the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is used to get the current datetime value.