C# - Queue
Queue is a special type of collection that stores the elements in FIFO style (First In First Out), exactly opposite of the Stack<T> collection. It contains the elements in the order they were added. C# includes generic Queue<T> and non-generic Queue collection. It is recommended to use the generic Queue<T> collection.
Queue<T> Characteristics
Queue<T>is FIFO (First In First Out) collection.- It comes under
System.Collection.Genericnamespace. Queue<T>can contain elements of the specified type. It provides compile-time type checking and doesn't perform boxing-unboxing because it is generic.- Elements can be added using the
Enqueue()method. Cannot use collection-initializer syntax. - Elements can be retrieved using the
Dequeue()and thePeek()methods. It does not support an indexer.
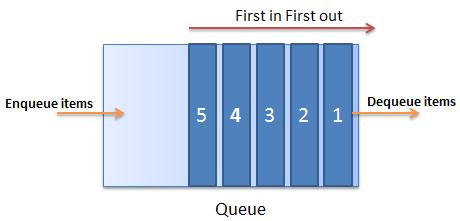
The following figure illustrates the Queue collection:
Creating a Queue
You can create an object of the Queue<T> by specifying a type parameter for the type of elements it can store. The following example creates and adds elements in the Queue<T> using the Enqueue() method. A Queue collection allows null (for reference types) and duplicate values.
Queue<int> callerIds = new Queue<int>();
callerIds.Enqueue(1);
callerIds.Enqueue(2);
callerIds.Enqueue(3);
callerIds.Enqueue(4);
foreach(var id in callerIds)
Console.Write(id); //prints 1234Queue<T> Properties and Methods
| Property | Usage |
|---|---|
| Count | Returns the total count of elements in the Queue. |
| Method | Usage |
|---|---|
| Enqueue(T) | Adds an item into the queue. |
| Dequeue | Returns an item from the beginning of the queue and removes it from the queue. |
| Peek() | Returns an first item from the queue without removing it. |
| Contains(T) | Checks whether an item is in the queue or not |
| Clear() | Removes all the items from the queue. |
Retrieve Elements from a Queue
The Dequeue() and the Peek() method is used to retrieve the first element in a queue collection. The Dequeue() removes and returns the first element from a queue because the queue stores elements in FIFO order. Calling the Dequeue() method on an empty queue will throw the InvalidOperation exception. So, always check that the total count of a queue is greater than zero before calling it.
Queue<string> strQ = new Queue<string>();
strQ.Enqueue("H");
strQ.Enqueue("e");
strQ.Enqueue("l");
strQ.Enqueue("l");
strQ.Enqueue("o");
Console.WriteLine("Total elements: {0}", strQ.Count); //prints 5
while (strQ.Count > 0)
Console.WriteLine(strQ.Dequeue()); //prints Hello
Console.WriteLine("Total elements: {0}", strQ.Count); //prints 0The Peek() method always returns the first item from a queue collection without removing it from the queue. Calling the Peek() method on an empty queue will throw a run-time exception InvalidOperationException.
Queue<string> strQ = new Queue<string>();
strQ.Enqueue("H");
strQ.Enqueue("e");
strQ.Enqueue("l");
strQ.Enqueue("l");
strQ.Enqueue("o");
Console.WriteLine("Total elements: {0}", strQ.Count); //prints 5
if(strQ.Count > 0){
Console.WriteLine(strQ.Peek()); //prints H
Console.WriteLine(strQ.Peek()); //prints H
}
Console.WriteLine("Total elements: {0}", strQ.Count); //prints 5Contains()
The Contains() method checks whether an item exists in a queue or not. It returns true if the specified item exists, otherwise returns false.
Contains() Signature: bool Contains(object obj);
Queue<int> callerIds = new Queue<int>();
callerIds.Enqueue(1);
callerIds.Enqueue(2);
callerIds.Enqueue(3);
callerIds.Enqueue(4);
callerIds.Contains(2); //true
callerIds.Contains(10); //false