PostgreSQL: INTERVAL Data Type
PostgreSQL support interval data type to store and manipulate period of time in years, months, days, hours, minutes, seconds, etc. Here years, months, and days are integer values where the seconds field can have fractional values.
PostgreSQL interval data type takes 16 bytes of storage that allows storing a period with a range from -178000000 years to 178000000 years.
@ interval [ <date_field(s)> ] [ (p) ]In the above syntax, <date_field(s)> is used to show the time period and p is used to display the precision value. The precision value is used for seconds and can range from 0 to 6. The sign above is optional.
The interval values can be written as shown below:
@ Interval '10 months after';
Interval '2 hours 15 minutes';In the below example, we will use interval datatype to get the 6 hours 30 minutes ago of last year from current time.
SELECT
now(),
now() - INTERVAL '1 year 6 hours 30 minutes'
AS "6 hours 30 minutes ago of last year";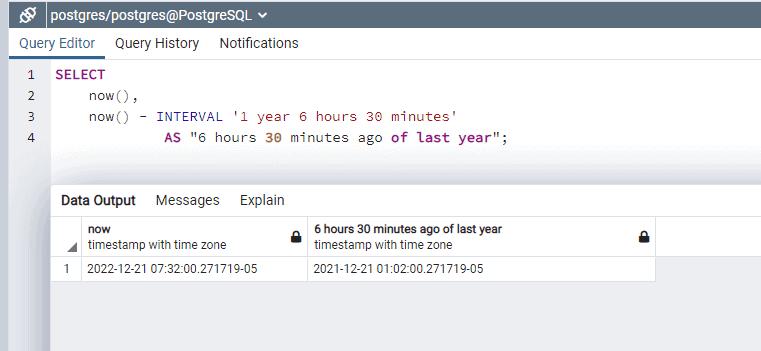
PostgreSQL Interval Output Formats
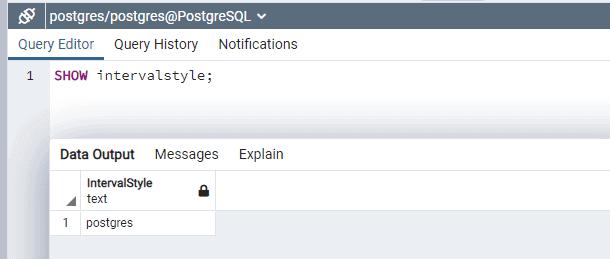
In PostgreSQL, the interval output format can be set by setting up the intervalstyle parameter.
You can check the current intervalstyle using the SHOW intervalstyle command.
Now when you do following select, you will get output as below:
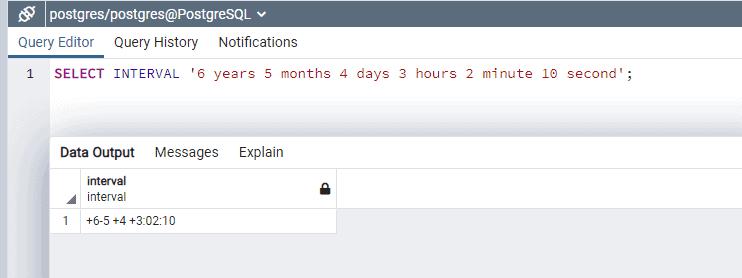
SELECT INTERVAL '6 years 5 months 4 days 3 hours 2 minute 10 second';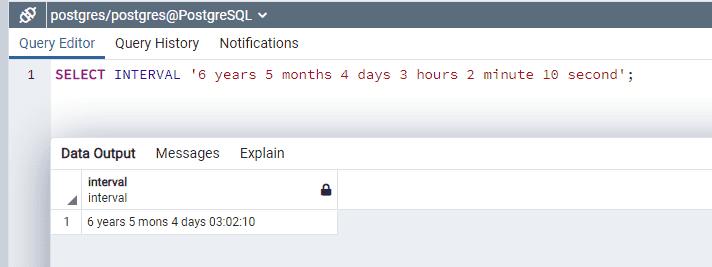
The intervalstyle can have these different output formats:
- postgres
- postgres_verbose
- sql_standard
- iso_8601
Let's set intervalstyle as sql_standard as shown below.
SET intervalstyle = 'sql_standard';Now, we can get the interval date as shown below:
Arithmetic Operations on Interval Type
Arithmetic operations like +, -, *, and / can be performed on interval datatype, as shown below.
SELECT
INTERVAL '2h 30m' + INTERVAL '5m' AS Addition,
INTERVAL '2h 30m' - INTERVAL '5m' AS Subtraction,
INTERVAL '5m' * 300 AS Multiplication,
INTERVAL '30m' / 10 AS Division;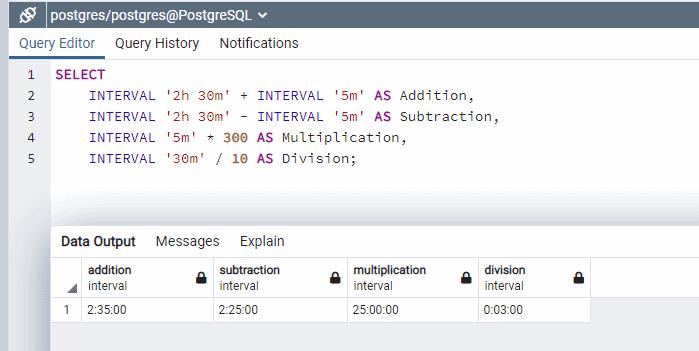
Extracting Data from Interval Type
PostgreSQL provides the EXTRACT() function to extract fields like a year, month, date, hour, minute, seconds, etc from interval values.
EXTRACT(<field> FROM <interval>)In above syntax, <field> can be year, month, date, hour, minute, seconds etc.
The following example extracts different interval data as year, month, and days.
SELECT
EXTRACT (YEAR FROM INTERVAL '6 years 5 months 4 days') AS YEAR,
EXTRACT (MONTH FROM INTERVAL '6 years 5 months 4 days') AS MONTH,
EXTRACT (DAY FROM INTERVAL '6 years 5 months 4 days') AS DAYS;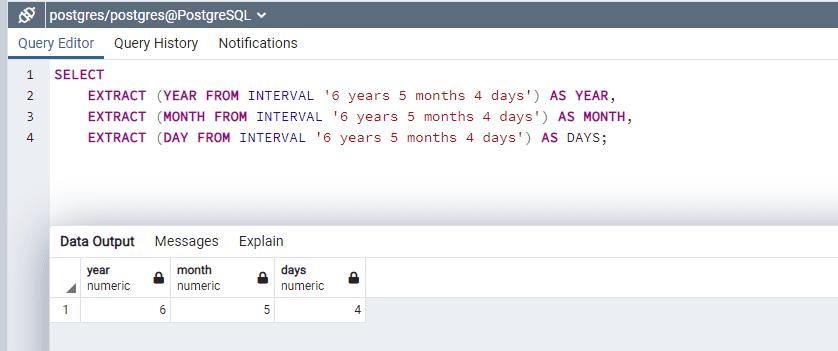
Adjust PostgreSQL Interval Values
PostgreSQL supports the following functions to modify interval values.
- justify_days(): Allows to modify interval of 30 days consider as month
- justify_hours(): Allows to modify interval of 24-hour consider as one day
- justify_interval(): Adjusts an interval using justify_days and justify_hours. It allows you to use additional sign adjustments to adjust the interval.
SELECT justify_days(INTERVAL '30 days'),
justify_hours(INTERVAL '24 hours'),
justify_interval(INTERVAL '6 months -5 hour');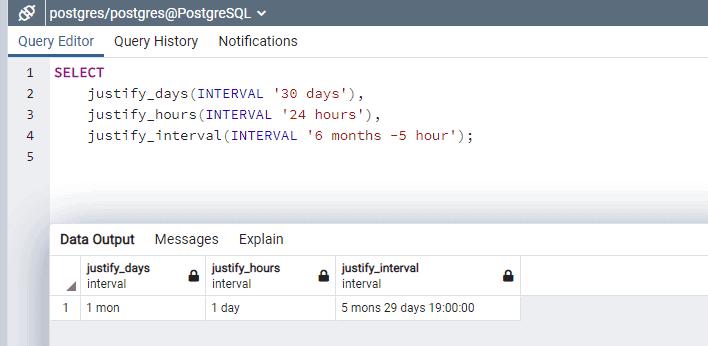
Convert Interval to String
We can use the TO_CHAR() function to convert the INTERVAL value to a string.
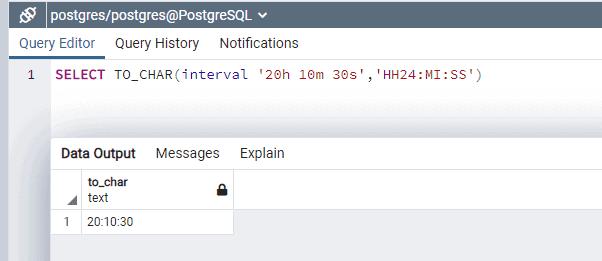
TO_CHAR(interval, format)The TO_CHAR() function takes two arguments, the first interval value and the second format in which you want to display the text.
SELECT TO_CHAR(interval '20h 10m 30s','HH24:MI:SS')