PostgreSQL: GREATEST() and LEAST()
In PostgreSQL, the GREATEST() function returns the largest value from the specified values and the LEAST() functions returns the smallest values from specified values. Both the functions take any number of arguments.
All the arguments or expressions must be convertible to a common data type, otherwise, it will raise an error.
Syntax
GREATEST(<argument1>, <argument2>,...)
LEAST(<argument1>, <argument2>,...)The following demonstrates the GREATEST() and LEAST() functions.
Example: GREATEST() and LEAST()GREATEST() and LEAST()
SELECT GREATEST(25, 6, 7, 10, 20, 54); -- returns 54
SELECT LEAST(25, 6, 7, 10, 20, 54); -- returns 6They work on the character data types also.
Example: GREATEST() and LEAST()
SELECT GREATEST('D','A', 'B', 'C','d','e','E'); -- returns 'E'
SELECT LEAST('D','A', 'B', 'C','d','e','E','a'); -- returns 'a'Consider the following Employee table.
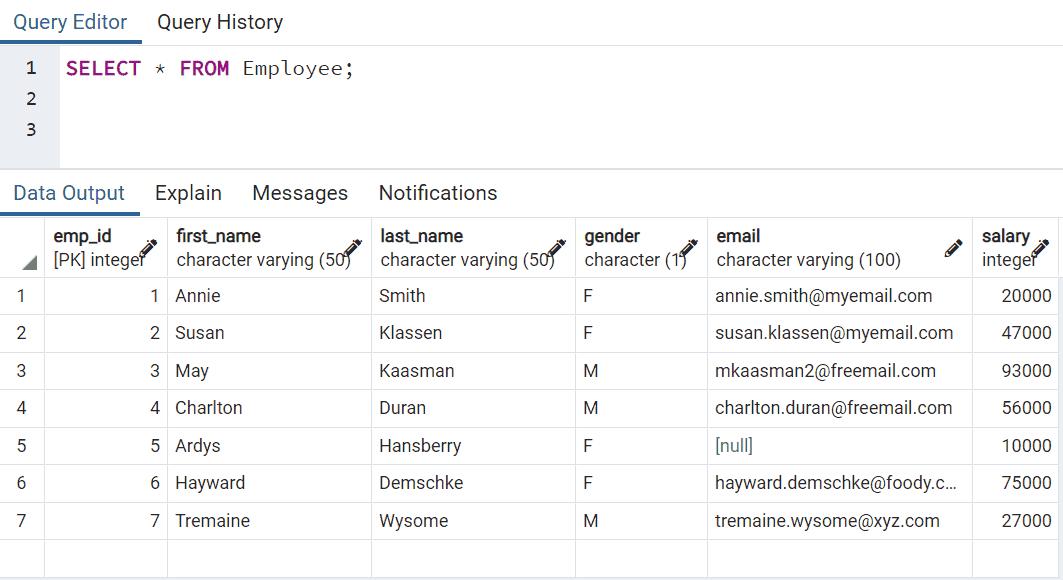
Now, the following finds the greatest and least values from first_name and last_name values.
Example: GREATEST() and LEAST()
SELECT GREATEST(first_name, last_name) AS LargeValue, LEAST(first_name, last_name) AS LeastValue FROM employee;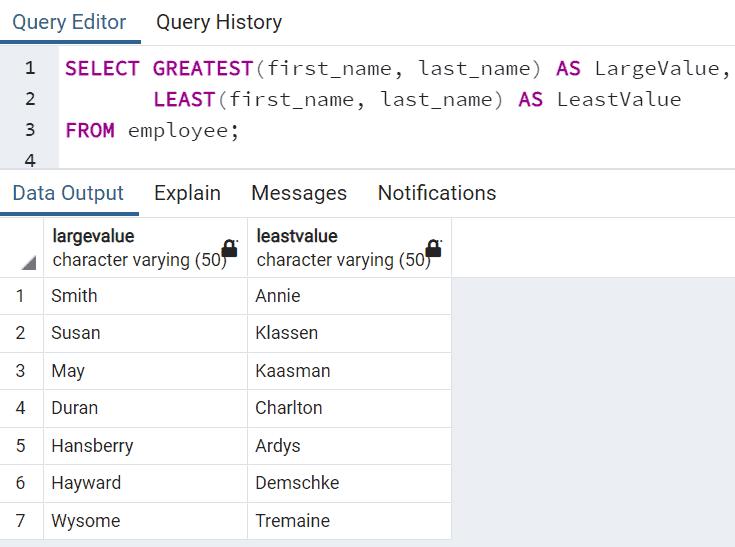
Both the functions ignore the NULL values. If all arguments are NULL, then return a NULL.
Example: GREATEST() and LEAST()
SELECT GREATEST(6, NULL); -- result: 6
SELECT LEAST(6, NULL); -- result: 6